The Egyptians believed that the earth (specifically Egypt) reflected the cosmos. The stars in the night sky and the constellations they formed were thought to have a direct bearing on one’s personality and future fortunes. The gods informed the night sky, even traveled through it, but were not distant deities in the heavens; the gods lived alongside the people of Egypt and interacted with them daily. Trees were considered the homes of the gods and one of the most popular of the Egyptian deities, Hathor, was sometimes known as “Mistress of the Date Palm” or “The Lady of the Sycamore” because she was thought to favor these particular trees to rest in or beneath. Scholars Oakes and Gahlin note that
“Presumably because of the shade and the fruit provided by them, goddesses associated with protection, mothering, and nurturing were closely associated with [trees]. Hathor, Nut, and Isis appear frequently in the religious imagery and literature [in relation to trees]”
Plants and flowers were also associated with the gods, and the flowers of the ished tree were known as “flowers of life” for their life-giving properties. Eternity, then, was not an ethereal, nebulous concept of some ‘heaven’ far from the earth but a daily encounter with the gods and goddesses one would continue to have contact with forever, in life and after death.
In order for one to experience this kind of bliss, however, one needed to be aware of the importance of harmony in one’s life and how a lack of such harmony affected others as well as one’s self. The ‘gateway sin’ for the ancient Egyptians was ingratitude because it threw one off balance and allowed for every other sin to take root in a person’s soul. Once one lost sight of what there was to be grateful for, one’s thoughts and energies were drawn toward the forces of darkness and chaos.
This belief gave rise to rituals such as The Five Gifts of Hathor in which one would consider the fingers of one’s hand and name the five things in life one was most grateful for. One was encouraged to be specific in this, naming anything one held dear such as a spouse, one’s children, one’s dog or cat, or the tree by the stream in the yard. As one’s hand was readily available at all times, it would serve as a reminder that there were always five things one should be grateful for, and this would help one to maintain a light heart in keeping with harmonious balance. This was important throughout one’s life and remained equally significant after one’s death since, in order to progress on toward an eternal life of bliss, one’s heart needed to be lighter than a feather when one stood in judgment before Osiris.
The Soul & The Hall of Truth
According to the scholar Margaret Bunson:
The Egyptians feared eternal darkness and unconsciousness in the afterlife because both conditions belied the orderly transmission of light and movement evident in the universe. They understood that death was the gateway to eternity. The Egyptians thus esteemed the act of dying and venerated the structures and the rituals involved in such a human adventure
The structures of the dead can still be seen throughout Egypt in the modern day in the tombs and pyramids which still rise from the landscape. There were structures and rituals after life, however, which were just as important.
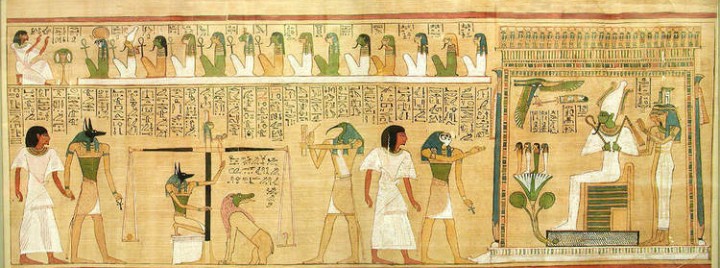
The soul was thought to consist of nine separate parts: the Khat was the physical body; the Ka one’s double-form; the Ba a human-headed bird aspect which could speed between earth and the heavens; Shuyet was the shadow self; Akh the immortal, transformed self, Sahu and Sechem aspects of the Akh; Ab was the heart, the source of good and evil; Ren was one’s secret name. All nine of these aspects were part of one’s earthly existence and, at death, the Akh (with the Sahu and Sechem) appeared before the great god Osiris in the Hall of Truth and in the presence of the Forty-Two Judges to have one’s heart (Ab) weighed in the balance on a golden scale against the white feather of truth.
One would need to recite the Negative Confession (a list of those sins one could honestly claim one had not committed in life) and then one’s heart was placed on the scale. If one’s heart was lighter than the feather, one waited while Osiris conferred with the Forty-Two Judges and the god of wisdom, Thoth, and, if considered worthy, was allowed to pass on through the hall and continue one’s existence in paradise; if one’s heart was heavier than the feather it was thrown to the floor where it was devoured by the monster Ammut (the gobbler), and one then ceased to exist.
Once through the Hall of Truth, one was then guided to the boat of Hraf-haf (“He Who Looks Behind Him”), an unpleasant creature, always cranky and offensive, whom one had to find some way to be kind and courteous to. By showing kindness to the unkind Hraf-haf, one showed one was worthy to be ferried across the waters of Lily Lake (also known as The Lake of Flowers) to the Field of Reeds which was a mirror image of one’s life on earth except there was no disease, no disappointment, and no death. One would then continue one’s existence just as before, awaiting those one loved in life to pass over themselves or meeting those who had gone on before.