Just like in any other civilization, the economy of Ancient Egypt relied on a variety of skilled and unskilled labor. There were many different careers available in Egypt, ranging from breaking rocks in mines to making scientific discoveries in a university. Over the course of 3,000 years, the ancient Egyptian empire remained remarkably stable. The same basic jobs were an essential part of ancient Egyptian civilization throughout the centuries.
Jobs for Slaves in Ancient Egypt
A lot of people are under the misconception that most jobs in ancient Egypt, particularly building the pyramids, was accomplished with slavery. The reality is that there were not that many slaves in Egypt until the Greeks conquered the nation and ended the ancient Egyptian dynasties. Only the wealthiest could afford to buy slaves from markets to do the work in their households. These slaves were typically prisoners of war.
Jobs in ancient Egypt for slaves included working in mines, plowing fields, cleaning households, watching a master’s children, tending gardens, or taking care of horses. Though slavery was rare, many peasants barely had more freedom than a slave. If they worked on land owned by a nobleman, they often gave him most of their crops, and their labor could be sold or rented along with the land.
Jobs Among the Egyptian Lower Class
Ancient Egypt jobs for peasants were very similar to jobs for slaves. However, they had more legal rights, and they could potentially rise through the social classes with a lot of diligence and effort. Though they had limited freedom, they did receive wages, had free time, and could make their own decisions about things like marriage or having children.
Farmers
Farming was the backbone of ancient Egyptian society, and it was one of the most common jobs. Some farmers worked the land of their local nobleman, while more prosperous ones posessed their own land that was passed on to their descendants.
Farming was usually a job that was done by the entire family. After each yearly flood of the Nile, farmers waited until the waters receded to plant their crops. The most common crops were wheat, corn, and barley. Farmers also planted vegetables, melons, pomegranates, figs, and flax. This was a tough and dangerous job because a farmer would lose their livelihood if the Nile failed to flood.

Illustration of Farmers in Ancient Egypt
Servants
Servants were people who were attached directly to the household of a higher-status Egyptian. Jobs for servants in ancient Egypt could include cooking, cleaning, running errands, babysitting children. Though being a servant was definitely one of the ancient Egypt jobs done by peasants, it was relatively comfortable. Though servants were subject to the whims of their masters, they had more reliable food sources than farmers.
Builders
Ancient Egyptian pharaohs were known for their massive building projects like obelisks and pyramids. At almost any time period, there were jobs in ancient Egypt for builders. Builders included all of the stonemasons, manual laborers, bricklayers, wood carvers, and mortar-mixers who would be needed in any building project. This was often exhausting work that required a lot of physical strength and endurance.
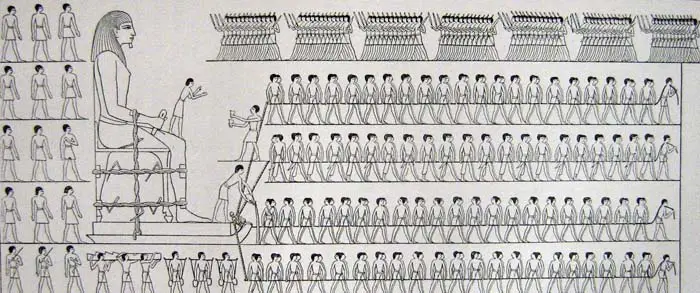
Depiction of workers moving a colossus
Common Soldiers
Any Egyptian who desired to join the military was allowed. This made it a highly sought after job for people who were tired of being farmers. Being a soldier came with many downsides since soldiers ran the risk of dying in battle.
Though being a soldier was risky, a man who distinguished himself in battle could potentially rise in the ranks and make a name for himself. However, the life of the soldier required hours of compulsory drilling and tough punishments for any man who fell behind, so it was not always pleasant.

Relief of Egyptian Soldiers



































