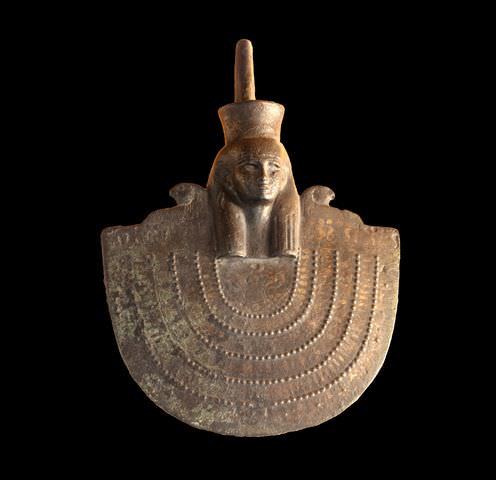
Neith (aka Net, Neit or Nit) and is one of the oldest deities of ancient Egypt who was worshipped early in the Pre-Dynastic Period (c. 6000 – 3150 BCE) and whose veneration continued through the Ptolemaic Dynasty (323 – 30 BCE), the last to rule
Neith (aka Net, Neit or Nit) and is one of the oldest deities of ancient Egypt who was worshipped early in the Pre-Dynastic Period (c. 6000 – 3150 BCE) and whose veneration continued through the Ptolemaic Dynasty (323 – 30 BCE), the last to rule
the dissolution of the central government at the start of the Third Intermediate Period (c. 1069-c. 525 BCE). This is the time of Imperial Egypt when it extended its reach beyond the former borders to create an empire. It is
The New Kingdom (c. 1570- c.1069 BCE) is the era in Egyptian history following the disunity of the Second Intermediate Period (c. 1782-1570 BCE) and preceding the dissolution of the central government at the start of the Third Intermediate Period (c. 1069-c. 525 BCE). This is the time
INTERVIEW WITH BISHOP SLIVANUS, OLD CAIRO This location is in a Fortress named the Fortress of Babylon. Its foundation is in the site where we stand today. Within the fortress are a lot of churches and other buildings: Abu Sarga,
Old Kingdom (c. 2686-2125 B.C) The division between the Early Dynastic Period and the Old Kingdom is artificial. Its first kings were descended from pharaoh Khasekhemwy. Egypt was almost self-sufficient with few outside enemies. The familial relations between some pharaohs are
Oum Ali is a very popular traditional dessert in Egypt. Oum Ali basically stands for “the mother of Ali.” It is an Egyptian bread and butter pudding that is made from butter, puff pastry and lots of cream and nuts. It
In his first encyclical letter “Deus Caritas Est” (God is love), Pope Benedict wrote: “Everything has its origin in God’s love, everything is shaped by it, everything is directed towards it.” The equivalent of what Benedict says about what God’s
Who Was Osiris? © Jan – Statue of Osiris Osiris was the ancient Egyptian god of the dead, the underworld, and the afterlife. He is usually depicted as a man with green skin and a beard associated with the pharaoh, wearing
Other Events Early in Xerxes I’s reign, Egypt rebelled against Persian rule. He took an army to Egypt to subdueit and left one of his brothers to rule Egypt. Xerxes I’s required all his territories to provide goods or troops for his invasion
Other Facts about the Ten Plagues of Egypt Some Biblical scholars contend that Thutmose III was the pharaoh of the Exodus because the Bible says that Joseph placed his brethren in the land of Ramses, which was around 1406 BC. They cite this as
2. Outline of a Program for Future Research Nevertheless, despite the progress that I have just outlined rapidly, the field of Islamic science as an academic discipline seems to get winded on the institutional level and suffers from a real
he 18th-century European travellers were fascinated with Egypt, its mysterious history, opulent arts and grandiose sites. These travellers often returned home with notes and drawings recording what they had seen, but although their accounts represented the start of Europe’s interest
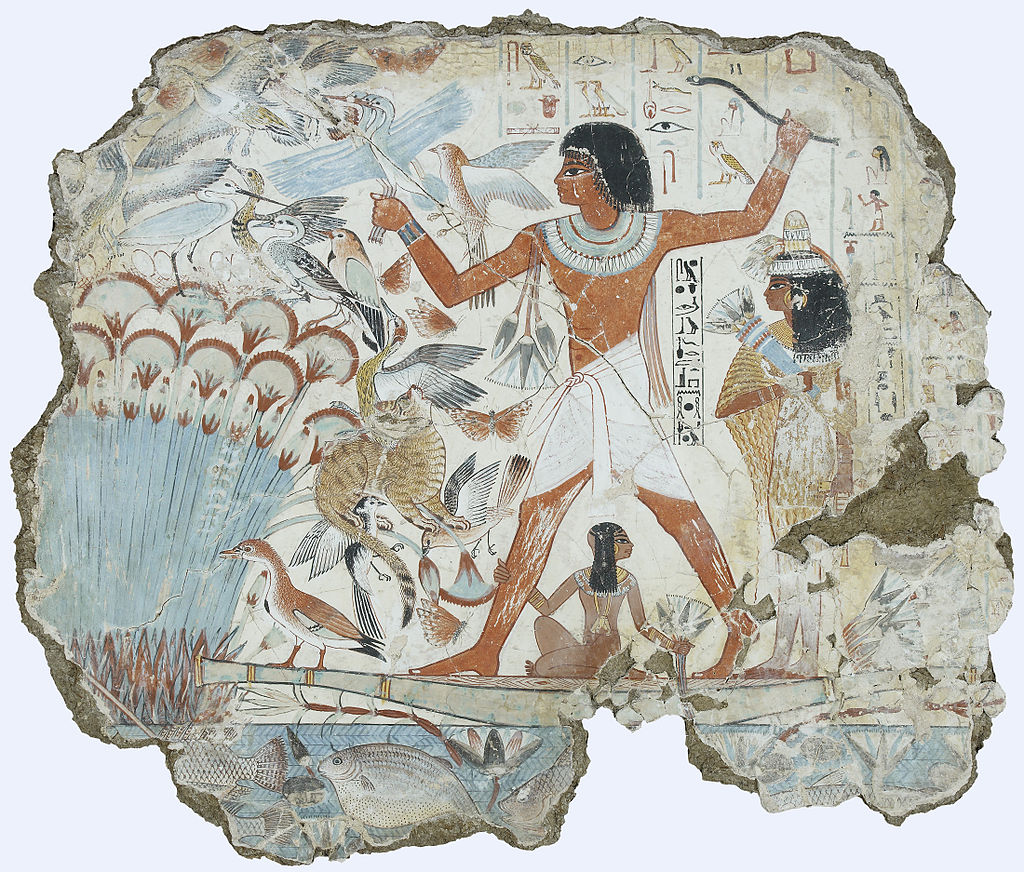
Not all Egyptian reliefs were painted, and less-prestigious works in tombs, temples and palaces were merely painted on a flat surface. Stone surfaces were prepared by whitewash, or if rough, a layer of coarse mud plaster, with a smoother gesso layer above; some finer limestones could
Paper and Writing Hieroglyphics The ancient Egyptians were among the first groups of people to write and keep records of events that happened in their lives. The earliest form of writing was in the form of hieroglyphics, which, simply put, were drawings
When we are looking at the feast scenes that are displayed on the walls of ancient Egyptian tombs, definitely noticeable are pale yellow hills that are depicted above heads of the feast participants. Generally, these hills are perceived as decorations of
Appearance was extremely important to ancient Egyptians and so was perfume and body fragrance. How someone smelled designed social, political and religious meaning. Egyptians have a long history of varied and exotic perfumes
Despite being known for long and peaceful reign within Egypt, Senusret I devoted his rule to offensively protecting Egypt’s borders. Egyptologists consider him the most powerful pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. Prepared for Power Senusret was
Predynastic Period (c.5300-3000 B.C.) Neolithic The first part of the Predynastic period is the Neolithic period. Agriculture became the main food source in the Nile Valley and communities worked together to raise food. Egyptologists discovered pits used to store grain. They also
There is much evidence of complex beliefs and practices in Ancient Egypt related to the important role fertility played in society. Religious beliefs included rules concerning purification, similar to other religions in the region. Women in Egypt were believed to
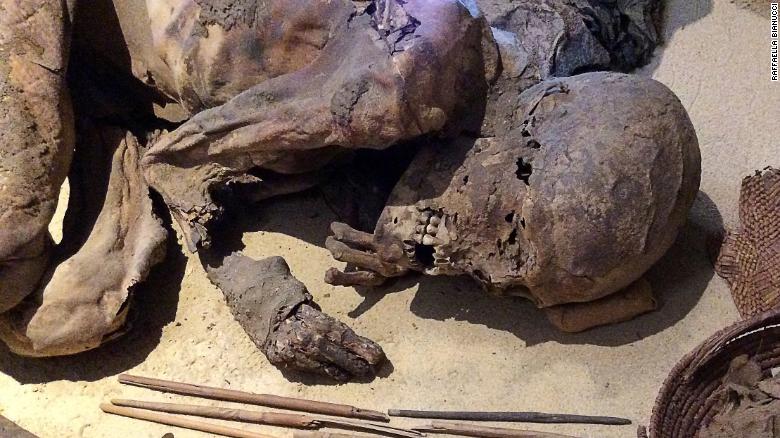
Last month, my colleagues and I published our analysis of an intact Egyptian prehistoric body, dating from around 3,700 to 3,500 BC, that had been housed in the Museo Egizio (Egyptian Museum) in Turin, Italy, since 1901. The results provide strong evidence that Egyptian
Flask Inv. No. 6717 Clay Presumably from Abu Menas, 5th / 6th century The pilgrimage site of Abu Menas is situated around 46 km southwest of Alexandria. St. Menas was martyred in the time of Emperor Diocletian (284-305). According to
Discoveries made since the end of the 19th century surrounding the (now submerged) ancient Egyptian city of Heracleum at Alexandria include a 4th century BC, unusually sensual, detailed and feministic (as opposed to deified) depiction of Isis, marking a combination
Hatshepsut (1479-1458 BCE) is considered to be one of ancient Egypt’s most revered if controversial rulers. Celebrated by Egyptologists as a commanding female sovereign whose rule ushered in a long period of military success, economic growth and prosperity. Hatshepsut was ancient Egypt’s
Hatshepsut, whose name means “Foremost of Noble Women” or “First Among Noble Women” (royal name, Ma’at-ka-re, translated as “spirit of harmony and truth”) was the fifth ruler of the 18th Dynasty ( ruled1479-1458 BCE). She was the daughter of Thuthmose I and
Nefertari means ‘beautiful companion’ and was the first of Rameses the Great’s Great Royal Wives. Known also as Nefertari Meritmutor or ‘Beloved of the goddess Mut’ Nefertari is one of Egypt’s most iconic queens, alongside Nefertiti, Hatshepsut and Cleopatra. However, comparatively little is known
Raised to Rule © Tiffany Silva – Statue of Queen Cleopatra For more than 300 years, Cleopatra’s family ruled Egypt. She was born the third child of King Ptolemy XII in 69 BC. Her name meant “glory of
Ramadan and Islam Like Muslims all over the world, Egyptian Muslims fast for the holy month of Ramadan. It is a time when they all come close to each other and respect each other, and it’s also a time when
Ramses II Biography: Architectural Accomplishments © Richard White – Ramesseum from the air Perhaps the best-known achievements of Ramses the Great are his architectural endeavors, most notable the Ramesseum and the temples of Abu Simbel. Ramses II’s interest in architecture resulted in the erection of more
The Red Sea coast is a beautiful area that runs up to Sharm-El-Sheikh and the interior Egyptian mainland before divering into the Gulf of Suez to the west and the Gulf of Aqaba up to Israel in the east. The many mountain ranges along
For Egyptians the decoration of tomb walls with reliefs or painted scenes provided some certainty of the perpetuation of life; in a temple, similarly, it was believed that mural decoration magically ensured the performance of important ceremonies and reinforced the memory of royal deeds. The earliest
Religion influenced nearly every aspect of the ancient Egyptians’ lives. As it was very important to them, they were bound by tradition and unwilling to change. The history of ancient Egyptian religion is rooted in Egypt’s prehistory and it lasted
There were no religious services in Egypt corresponding to worship services in the present day. The priests served the gods, not the people, and their job was to administer to the gods’ daily needs, recite hymns and prayers for the
For most of ancient Egypt’s history, it observed a polytheistic form of religious worship. With 8,700 gods and goddesses, people were allowed to venerate any deity of their choice. Many worshipped several deities. The appeal of some deities spread throughout Egypt,
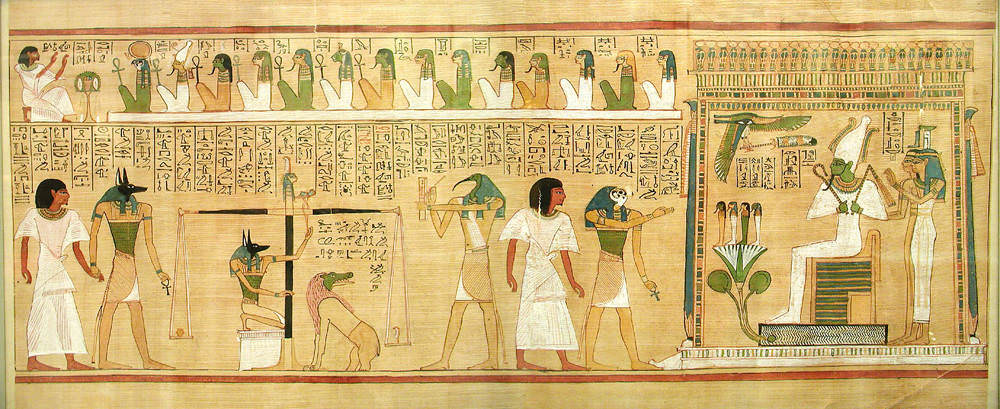
Instructions on how one would animate a shabti in the next life, as well as how to navigate the realm which waited after death, was provided through the texts inscribed on tomb walls and, later, written on papyrus scrolls. These are
Hieroglyph Symbol Meaning Vulture Represents the Egyptian Vulture Foot Human foot and lower leg Hand Word for hand, actions or actions that are performed Also used in iconography (Flowering) Reed Ideogram, alphabetic uniliteral (consisting of one letter only) vowel ‘i’
Reputation in History © Nick Taylor – Relief of Xerxes I Modern and ancient scholars often portray Xerxes I as a tyrant. His rule over ancient Egypt was harsh, disregarding local customs and beliefs left and right. Xerxes decided not to
Ma’at ruled everything, which made her a very busy goddess. Every day she helped Ra to steer his boat across the sky, making a path for the sun. She was the partner of Thoth and the mother of the eight
The Romans controlled such a vast empire for so long a period that a summary of the art produced in that time can only be a brief and selective one. Perhaps, though, the greatest points of distinction for Roman art are its very diversity,
@ Jason Devaun – Cleopatra, depiction on a Ptolemaic coin Roman Invasion While Cleopatra fought to regain control of Egypt, the Roman guardian Pompey was fighting his own battles against his fellow Romans. Pompey sought refuge with Ptolemy XIII only to be murdered the