Art is an essential aspect of any civilization. Once the basic human needs have been taken care of such as food, shelter, some form of community law, and a religious belief, cultures begin producing artwork, and often all of these developments occur
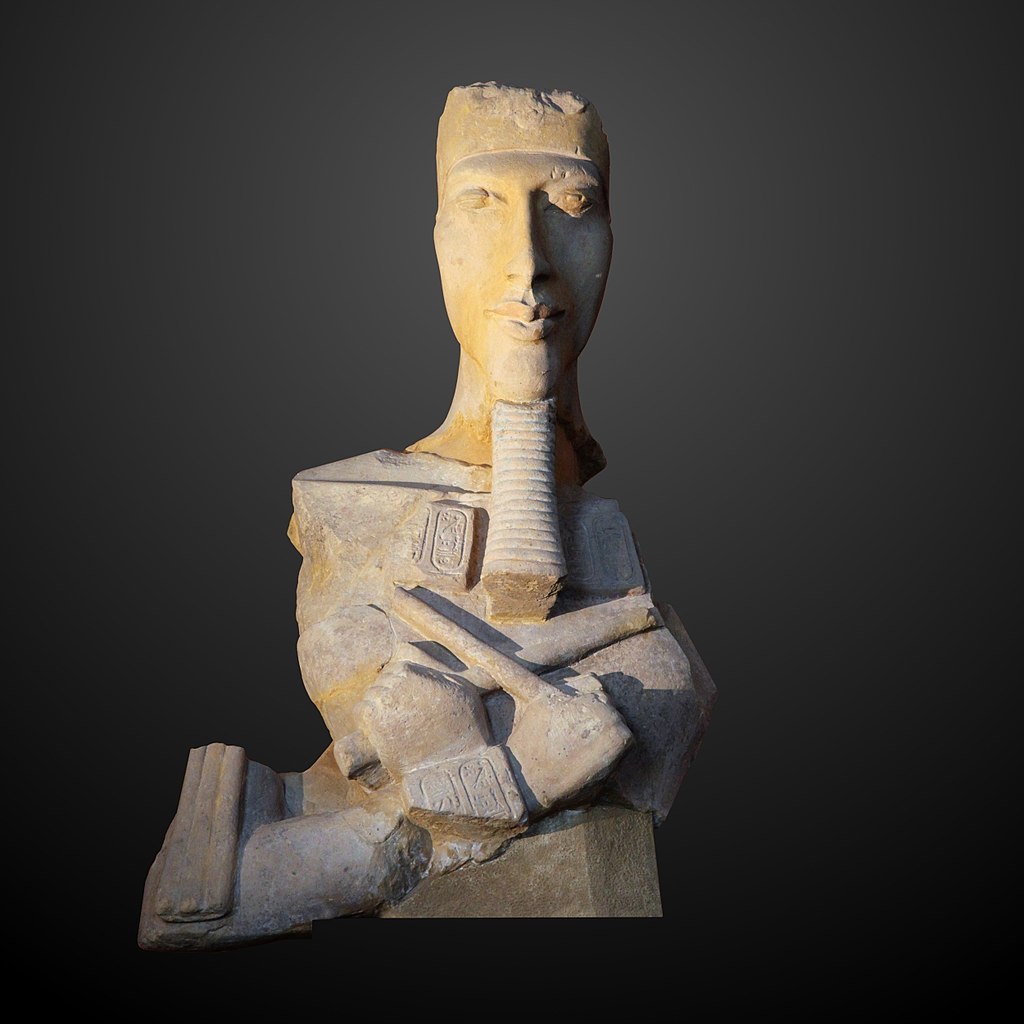
The Amarna period is named for the extensive archeological site at Amarna, where pharaoh Akhenaten moved the capital in the late Eighteenth Dynasty. This period, and the years leading to it, form the most drastic interruption to the continuity of style in the Old
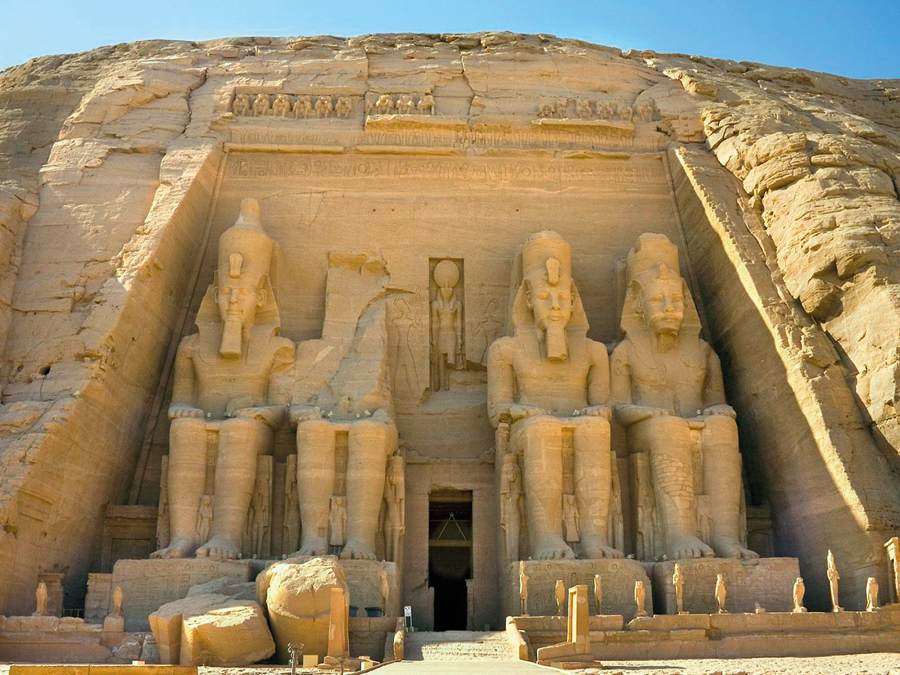
The pyramids are the most recognizable symbol of ancient Egypt. Even though other civilizations, such as the Maya or the Chinese, also employed this form, the pyramid in the modern day is synonymous in most people’s minds with Egypt. The pyramids at Giza remain impressive monuments thousands of years
The artworks of ancient Egypt have fascinated people for thousands of years. The early Greek and later Roman artists were influenced by Egyptiantechniques and their art would inspire those of other cultures up to the present day. Many artists are known from later periods but those of
The ancient Egyptians were best known for their pyramids. These impressive and stately works of architecture are not only grand displays of art themselves, they also represent incredible mathematical and technological knowledge. Over 80 pyramids still stand today that are over 3,000
Examples of ancient Egyptian art and crafts still exist today. They have survived the ravages of thousands of years and are prime examples of the dedication craftsmen felt for their art. Unfortunately, items crafted from leather, wood and other perishables have
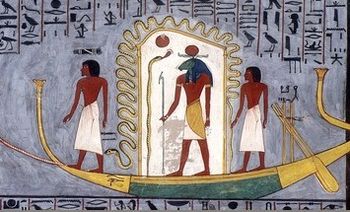
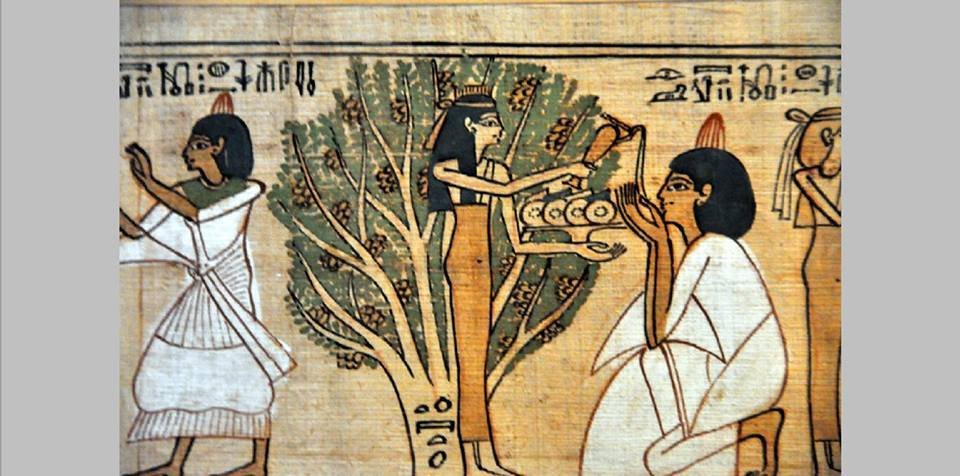
Since the Ancient Egyptians were highly religious people, much of the art they created can be found on temple walls and in tombs in the form of sculptures and paintings. The paintings in tombs were meant to help guide the
Ancient Egyptian art is five thousand years old. It emerged and took shape in the ancient Egypt, the civilization of the Nile Valley. Expressed in paintings and sculptures, it was highly symbolic and fascinating – this art form revolves
Ancient Egyptian art is five thousand years old. It emerged and took shape in the ancient Egypt, the civilization of the Nile Valley. Expressed in paintings and sculptures, it was highly symbolic and fascinating – this art form revolves round
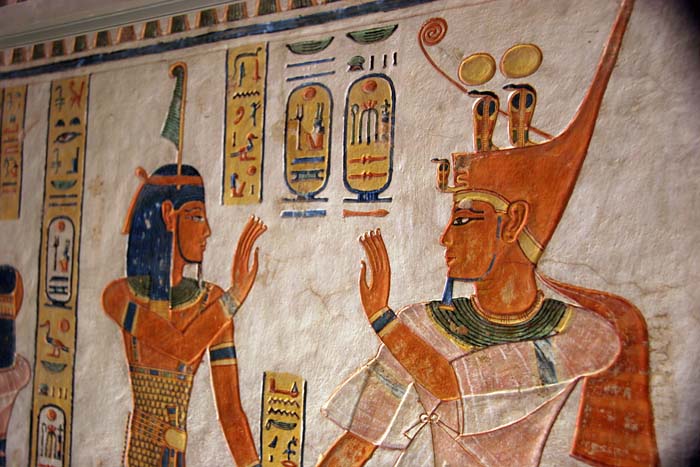
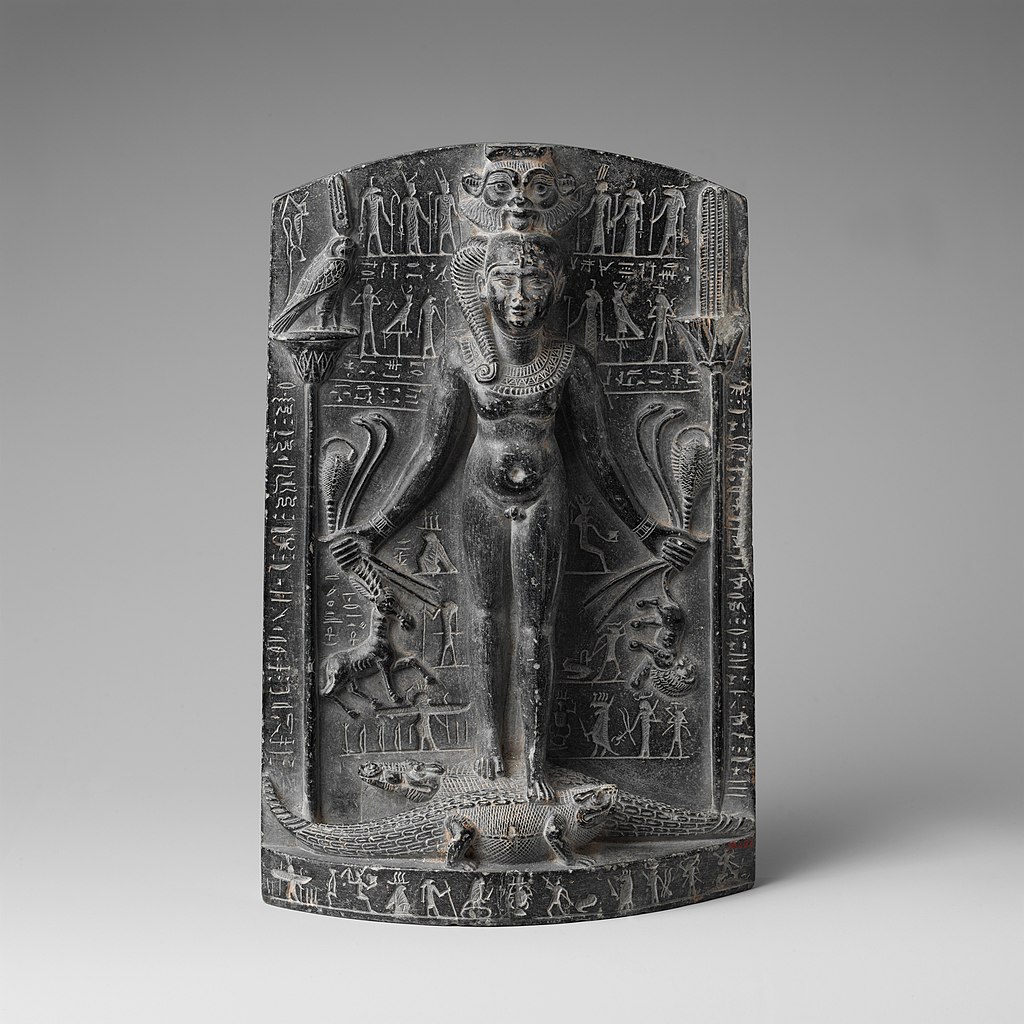
Religion in ancient Egypt was fully integrated into the people’s daily lives. The gods were present at one’s birth, throughout one’s life, in the transition from earthly life to the eternal, and continued their care for the soul in the afterlife of the Field
Ancient Egyptian art must be viewed from the standpoint of the ancient Egyptians to understand it. The somewhat static, usually formal, strangely abstract, and often blocky nature of much Egyptian imagery has, at times, led to unfavorable comparisons with later,
Gifted women actively participated in the weaving, grieving, and music organizations in Ancient Egypt. Moreover, being a professional in entertainment was another job that was occupied by women in Ancient Egypt (Hunt, 2009).Yet; there is no proof
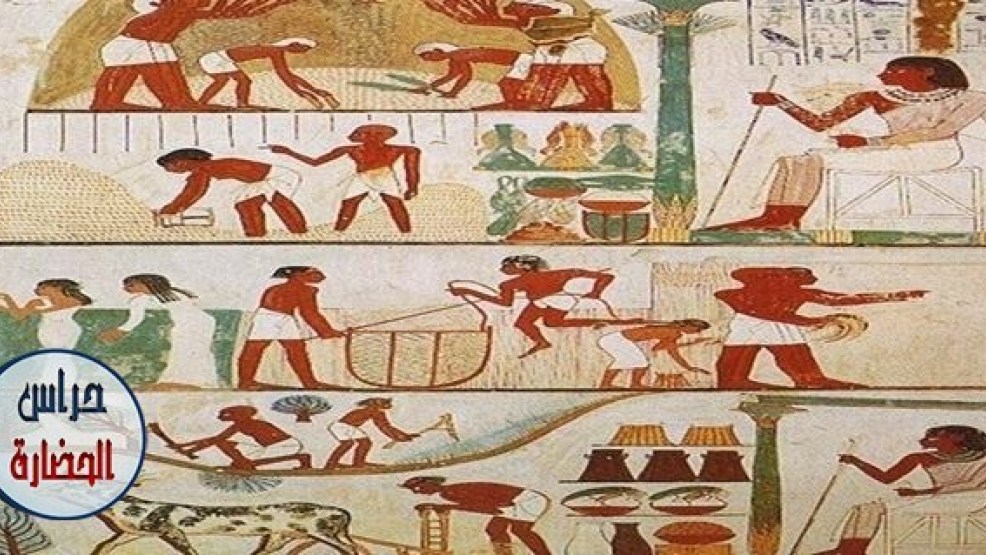
A lot of what we know about the Ancient Egyptians comes from their art. From the many pieces of art they created we can learn things like what they looked like, what kind of clothes they wore, what jobs they
A lot of what we know about the Ancient Egyptians comes from their art. From the many pieces of art they created we can learn things like what they looked like, what kind of clothes they wore, what jobs they
The First Intermediate Period has long been characterized as a time of chaos and darkness and artwork from this era has been used to substantiate such claims. The argument from art rests on an interpretation of First Intermediate Period works
The First Intermediate Period has long been characterized as a time of chaos and darkness and artwork from this era has been used to substantiate such claims. The argument from art rests on an interpretation of First Intermediate Period works
The Naqada III period, from about 3200 to 3000 BC,[8] is generally taken to be identical with the Protodynastic period, during which Egypt was unified Naqada III is notable for being the first era with hieroglyphs (though this is disputed by some), the first regular
The Naqada III period, from about 3200 to 3000 BC,[8] is generally taken to be identical with the Protodynastic period, during which Egypt was unified. Naqada III is notable for being the first era with hieroglyphs (though this is disputed by some), the first regular use
Pre-Dynastic Egypt, corresponding to the Neolithic period of the prehistory of Egypt, spanned from c. 6000 BC to the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period, around 3100 BC. Continued expansion of the desert forced the early ancestors of the Egyptians to settle around the Nile and adopt a more sedentary lifestyle during the Neolithic.
Pre-Dynastic Egypt, corresponding to the Neolithic period of the prehistory of Egypt, spanned from c. 6000 BC to the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period, around 3100 BC. Continued expansion of the desert forced the early ancestors of the Egyptians to settle around the Nile and adopt a more sedentary lifestyle during the Neolithic.
Egyptian art is known for its distinctive figure convention used for the main figures in both relief and painting, with parted legs (where not seated) and head shown as seen from the side, but the torso seen as from the front. The
The different colors below are listed with their Egyptian name following, the materials used in creating them, and what they symbolized. The definitions follow the work of Richard H. Wilkinson in his Symbolism & Magic in Egyptian Art and Margaret Bunson’s Encyclopedia of Ancient
The different colors below are listed with their Egyptian name following, the materials used in creating them, and what they symbolized. The definitions follow the work of Richard H. Wilkinson in his Symbolism & Magic in Egyptian Art and Margaret Bunson’s Encyclopedia of Ancient
The ancient Egyptians had a great appreciation for life which is clearly depicted through their art. Images of people enjoying themselves – whether in this life or the next – are as plentiful as those most often seen of the
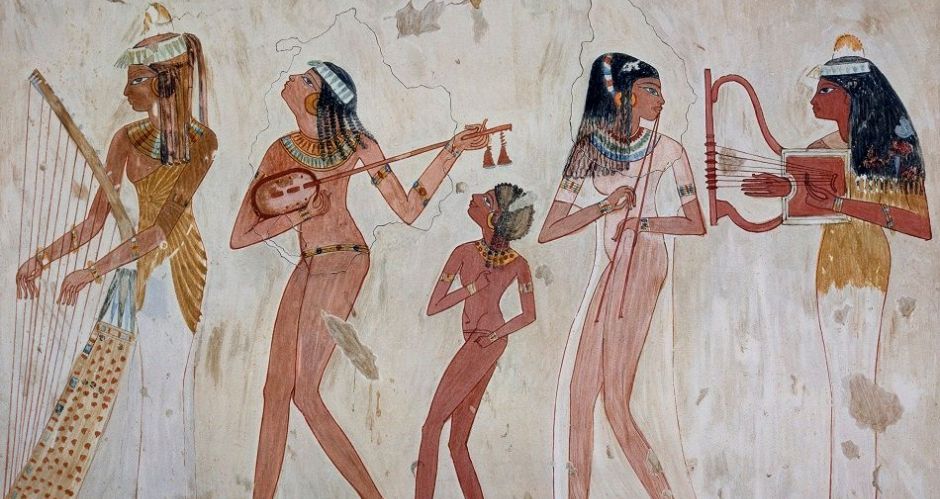
By the time of the New Kingdom of Egypt (c. 1570 – c. 1069 BCE) music was well established as a part of Egyptian life. The famous poetic genre of the love song, so closely associated with the New Kingdom, may have developed
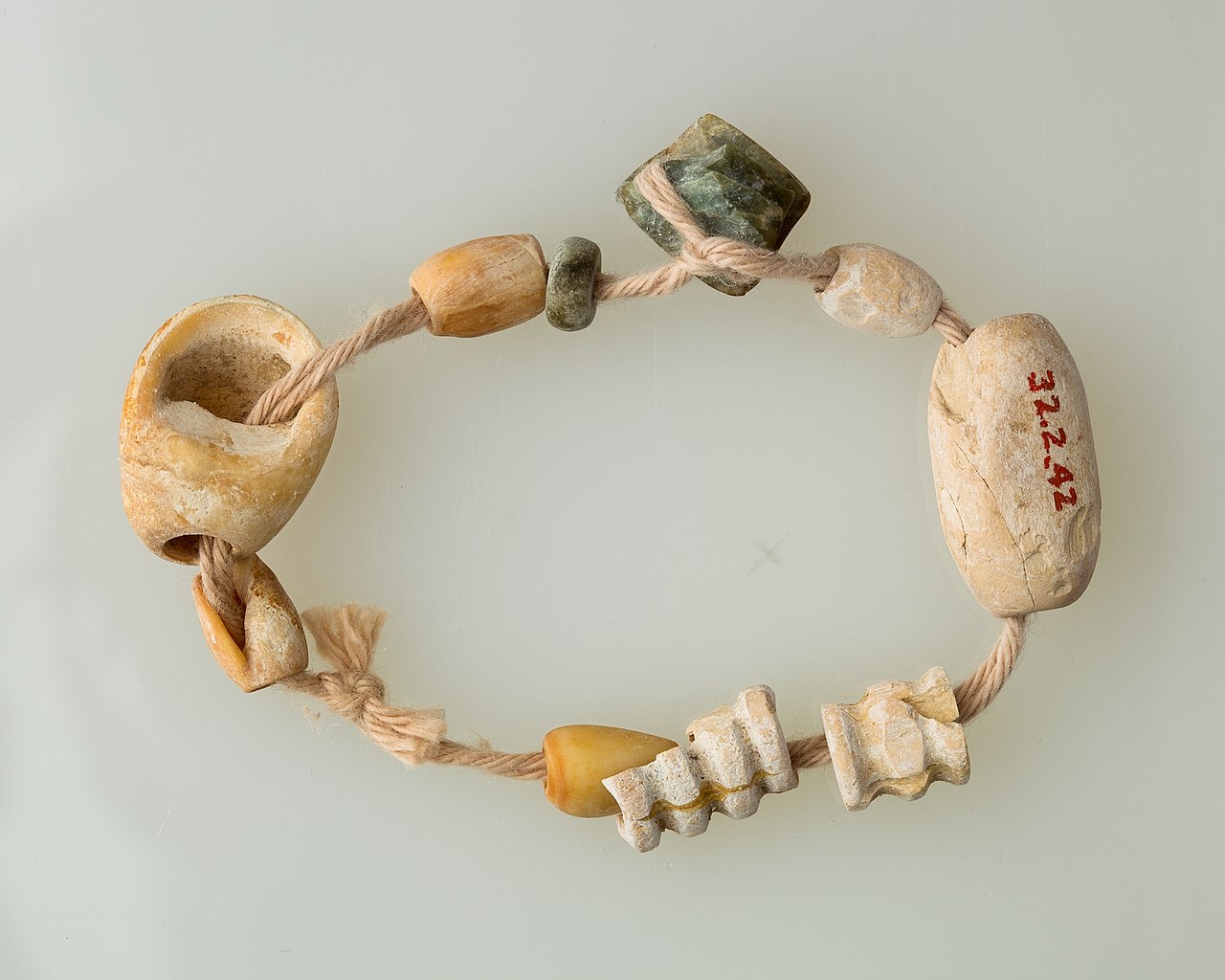
Gold provided Egyptian jewelry with its richness; it was used for settings, cloisonné work, chains, and beads, both solid and hollow. Soldering, granulation, and wire making were practiced. Precious stones were not used, but a wide range of semiprecious stones was exploited: carnelian, amethyst, garnet, red and yellow jasper, lapis lazuli, feldspar, turquoise, agate.
Mud brick and wood were the standard materials for houses and palaces throughout the Dynastic period; stone was used occasionally for such architectural elements as doorjambs, lintels, column bases, and windows. The best-preserved private houses are those of modest size
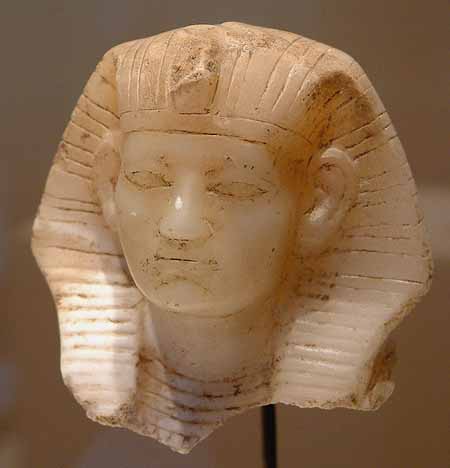
Egyptian art and architecture, the ancient architectural monuments, sculptures, paintings, and decorative crafts produced mainly during the dynastic periods of the first three millennia BCE in the Nile valley regions of Egypt and Nubia. The course of art in Egypt paralleled to a large extent
Egyptian art and architecture, the ancient architectural monuments, sculptures, paintings, and decorative crafts produced mainly during the dynastic periods of the first three millennia BCE in the Nile valley regions of Egypt and Nubia. The course of art in Egypt paralleled to a large extent
El-Fishawy Café is one of Cairo’s famous cafes. It is located in the Al-Azhar neighborhood and is considered one of the oldest cafes in Cairo, since its establishment dates back to 1797 AD. The cafe took its fame and luster,
The great temples of ancient Egypt arose from the same technological skill one sees on the small scale of household goods. The central value observed in creating any of these goods or structures was a careful attention to detail. The
Harper’s songs were lyrics composed in ancient Egypt to be sung at funeral feasts and inscribed on monuments. They derive their name from the image which accompanies the text on tomb or chapel walls, stelae, and papyri in which a blind harper is shown
The art of Egypt is the story of the elite, the ruling class. Throughout most of Egypt’s historical periods those of more modest means could not afford the luxury of artworks to tell their story and it is largely through
The nude figure is a universal visual theme, deeply rooted in the history of art, and it is seemingly ubiquitous in the art of the ancient civilizations of the Near East and Mediterranean. The Antikenmuseum, in Basel, Switzerland, recently opened a new exhibition – Naked!
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Create a timeline of ancient Egyptian civilization, marking the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms KEY TAKEAWAYS Key Points Ancient Egyptian art reached considerable sophistication in painting and sculpture , and was both highly stylized and symbolic. The Nile
Roman Sculpture Roman sculpture blended the idealised perfection of earlier Classical Greek sculpture with a greater aspiration for realism and mixed in the styles prevalent in Eastern art. Roman sculptors have also, with their popular copies of earlier Greek masterpieces, preserved for posterity invaluable works
Egyptian artists used a wide array of materials, both local and imported, from very early in their history. For instance, already in the Predynastic period we find figurines carved from lapis lazuli—a lustrous blue stone that originates in what is
Two-dimensional art represented the world quite differently. Egyptian artists embraced the two-dimensional surface and attempted to provide the most representative aspects of each element in the scenes rather than attempting to create vistas that replicated the real world. Each object
Music and dance were highly valued in ancient Egyptian culture, but they were more important than is generally thought: they were integral to creation and communion with the gods and, further, were the human response to the gift of life and all
The Naqada culture is an archaeological culture of Chalcolithic Predynastic Egypt (c. 4400–3000 BC), named for the town of Naqada, Qena Governorate. It is divided into three sub-periods: Naqada I, II and III. Naqada The Amratian (Naqada I) culture lasted from about 4000 to 3500 BC. Black-topped ware continues to