Ancient Egyptian Agriculture
Agriculture was the foundation of the ancient Egyptian economy and vital to the lives of the people of the land. Agricultural practices began in the Delta Region of northern Egyptand the fertile basin known as the Faiyum in the Predynastic Period in Egypt (c. 6000 – c. 3150 BCE), but there is evidence of agricultural use and overuse of the land dating back to […]

Isis | The Goddess of Fertility
Isis was the ancient Egyptian goddess of marriage, fertility, motherhood, magic and medicine. Many myths and legends exist about Isis in Egypt and Egyptian literature uses several names and titles for this goddess. Worship of Isis, her temples and her cult spread through Egypt and parts of Europe. Names, Titles & Roles Isis is the “Goddess […]

Daily Life in Ancient Egypt
When we think of ancient Egyptians, the image that most readily pops into our minds is hordes of workers labouring to build a colossal pyramid, while whip-wielding overseers brutally urge them onwards. Alternatively, we imagine Egyptian priests chanting invocations as they conspired to resurrect a mummy. Happily, the reality for ancient Egyptians was quite different. […]
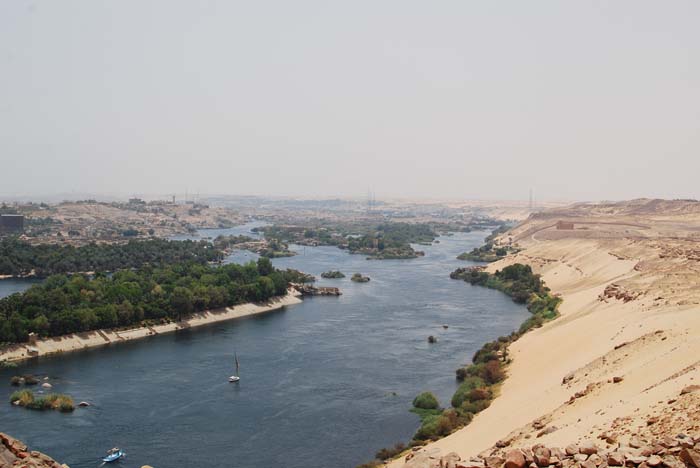

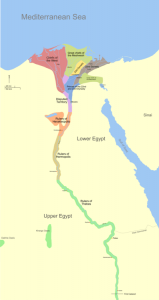
The Nile River in Ancient Egypt
The Nile River has certainly played a critical role in the history of ancient Egypt. Famous as the longest river in the world, the river got its name from the Greek word Neilos, which means valley. The Nile floods the lands in Egypt, leaving behind black sediment. That’s why the ancient Egyptians named the river Ar, meaning […]

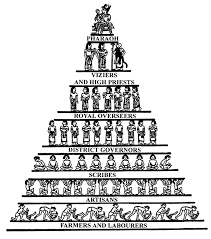
Ancient Egypt’s Social Pyramid
The Pharaoh High government officials like the vizier (the pharaoh’s right hand man), the chief treasurer and the army general Priests and nobles (who serve as lesser government officials) Soldiers and scribes (who write down important events and calculate taxes) Craftsmen and merchants Farmers and unskilled workers Slaves Often, people from a single level would live in […]